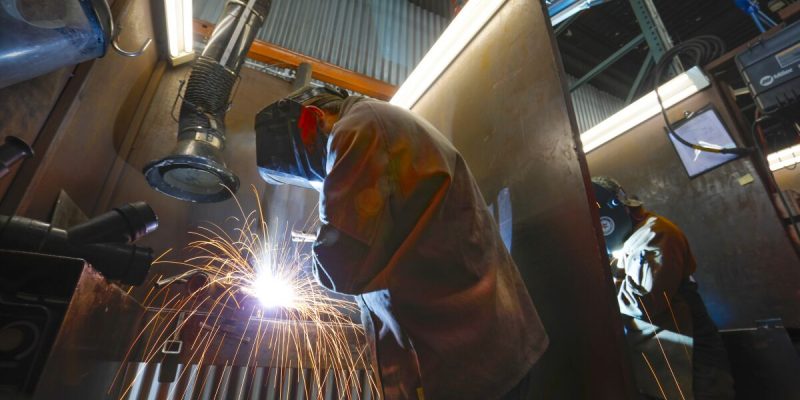
There are multiple prominent welder San Diego manufacturers, similar to Ford, Toyota, and Mercedes Benz in the vehicle business. Lincoln, Miller, Hobart, and ESAB are the major boys.
There are various “models” of welding machines, just as there are sedans, trucks, sports coupes, and SUVs. Each serves a distinct function and caters to different users.
Choosing the best one for you does not have to be difficult. The information provided here can assist you in navigating the procedure.
welder San Diego Varieties
The following are the most often used welders:
- inert metal gas (MIG)
- inert tungsten gas (TIG)
- oxy-acetylene welders (“gas” or “oxyfuel”)
- welding using a shielded metal arc (“SMAW” or Stick)
There are also more versatile, more expensive multi-process welding equipment that can weld using multiple welding processes. There are also engine-driven welders for work away from the electricity grid.
Step 1: Determine the metal you will be welding with
Steel made of carbon
The vast majority of welding are performed on carbon steel pipe or sheet metal. Carbon steel can withstand high temperatures. As a result, unlike the other metals described below, this metal is fairly forgiving when a beginner welder applies excessive heat.
Steel, stainless
When it comes to heat, stainless steel (“SS”) is pickier. Because of its anti-corrosion qualities, manufacturers utilise this alloy, which is composed of steel, chromium, and nickel, for food/beverage containers and many other goods.
Aluminum
Aluminum conducts heat as well as a non-ferrous metal that you always need more of it to maintain your puddle molten. At the same time, if the work piece becomes too hot, it distorts readily.
Titanium
Titanium, Chromoly, and other exotic metals have unique temperature sensitivity challenges that welders must address.
Step 2: Define a current range that encompasses all possible metal thicknesses
The more current required to weld a junction with good penetration, the thicker the metal.
Because the cost of a welding machine is determined in part by how much power it produces, you must plan ahead of time the maximum thickness of base metals and fixtures you will be working on in your shop.
A 1/8′′ (.125 in) mild steel sheet, for example, requires around 125 amps.
Step 3: Determine Where You Will Weld
Knowing where you will be welding most of the time influences what kind of equipment you should get.
There are several aspects to consider:
Power Source
If you plug the machine into the wall, you have the following options:
110/120 volt alternating current (AC) – This is the normal electricity supplied to all utility company customers, whether residential and commercial.
Most welding equipment need a high-power, 30-amp circuit that is 220/240 volts AC. This is available at any industrial area. Residential wiring is a different story.
Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase – Most electrical equipment is built for typical “single phase” operation, drawing from the 220-240 voltage line coming off the grid.
Off-Grid Situation
If you’re welding outside and don’t have access to a power source, you’ll need an engine-driven welder or a welder-generator to finish the job.
Windy Weather
If you anticipate welding in unsheltered places where a wind is probable, your welds may suffer as a result.
The CO2/argon gas utilized in the MIG process to protect the molten puddle of a weld would be blasted away and rendered useless.
Step 4: Recognize and Compare Key Features
Reading the sales material for various welders might be difficult because of the language and sales pitch.
However, there are a few key characteristics to look for:
The Duty Cycle
This specification specifies how much continuous welding a machine can complete in 10 minutes.
Traditionally, duty cycle is defined as the number of minutes a welder can weld at the greatest current the machine delivers in a 10-minute period.
Voltage in an Open Circuit
When no current is flowing, this is the voltage emitted by an arc welding torch or gun.
On the one hand, having a live circuit hanging about on the workbench with the potential to inflict catastrophic injury is risky.
Thermal Overload Defense
A machine either has it or does not, and you should only buy one that does. If the circuit within your torch or gun overheats, this function will immediately remove power to it.
Step 5: Determine if compressed gases are required
For various welding operations, various gases or gas combinations are employed. The kind of gas required for MIG welds is determined by the technique, the base metal, the welding position, and the ambient conditions.
Conclusion
These procedures will not only guide you through the process of choosing a welder San Diego. You’ll learn about the different units and what works best in certain scenarios.
















Comments